A protocol means set of rules and guidelines for some particular task. In computing (Computer science), a protocol or communication protocol is a set of rules in which computers communicate with each other. The protocol says what part of the conversation comes at which time. Some examples of internet protocols are-
• HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
• HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secured)
• TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol)
• FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
• IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol)
• POP (Post Office Protocol)
• SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
• TELNET (Telecommunications Network)
• UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
• NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol)
• MAC (Media Access Control protocol)
• DNS (Domain Name System protocol)
• DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
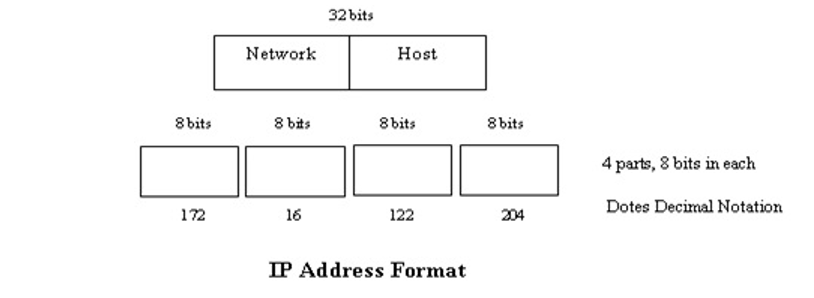
In widely installed phase of the Internet Protocol (IP) today, an IP address is a 32-bit number that recognize each sender or receiver of information that is sent in packets across the Internet. When you request an HTML page or send e-mail, the Internet Protocol part of TCP/IP consist your IP address in the message (actually, in each of the packets if more than one is required) and sends it to the IP address that is obtained by looking up the domain name in the url you can requested or in the e-mail address you're sending a message. At the other end, host can see the IP address of the Web page requestor or the e-mail sending host and can reply by sending another message using the IP address it fetched. 32 bits IP address categories into parts network id and host id.
The 32-bit IP address is clubbed eight bits at a time, separated by dots and represented in decimal format. This is known as dotted decimal technique as shown in figure below. The 32-bit number is separated in two parts as Network part and Host part.
The Network part of the Internet Protocol Address-
The Internet is particularly the interconnection of many individual networks (it's sometimes referred to as an internetwork). So, the Internet Protocol (IP) is primarily the collection of protocols for one network communicating with any other. Each network must know its own address on the Internet and that of any other networks with which it communicates. To be component of the Internet, a group needs an Internet network number. This expulsion network number is in any packet combined out of the network onto the Internet.
The Local or Host Part of the IP Address-
In addition to the network address or number, information is need about which particular host in a network is sending or receiving an information. So, the IP address requires both the unique network number and a host number (which is unique within the network). The host number is most of the times called a local address. Element of the local address can be identified a sub network or subnet address, which makes it easier for a network that is categorized into mainly physical subnetworks (for examples, several different local area networks) to handle many devices. This IP addresses divided into four classes.
IP Address Classes and Their Formats-
Since networks vary in size, there are four different address formats or classes to consider when applying to NIC for a network number as
• Class A addresses are for large networks with many devices.
• Class B addresses are for medium-sized networks.
• Class C addresses are for small networks (fewer than 256 devices).
• Class D addresses are multicast addresses
The first few bits of each IP address indicate which of the address class formats it is using. The address structures look like this:
Class A
![]()
Note-
Ques1: What is the total number of IP addresses present in class A?
Ans1: IP address is 32 bit number in which first bit is fixed so we have only 31 bits. Using 31 bit we can generate 231 numbers. So class A has 231 IP addresses.
Ques2: How many networks present in class A?
Ans2: Class A has 128 networks.
Ques3: Range of class A?
Ans3: Range of class A (1-126).
Class C
![]()
Note-
Ques1: What is the total number of IP address present in class C?
Ans1: IP address is 32 bit number in which first three bit is fixed and then we have only 29 bits. Using 29 bit we can generate 229 numbers. So class C has 229 IP addresses.
Ques2: How many networks present in class C?
Ans2: Class C has 221 networks.
Ques3: Range of class C?
Ans3: Range of class C (192-223).
Class D
![]()
Note-
Ques1: What is the total number of IP address present in class D?
Ans1: IP address is 32 bit number in which first four bit is fixed and then we have only 28 bits. Using 28 bit we can generate 228 numbers. So, class D has 228 IP addresses.
Ques2: How many networks present in class D?
Ans2: Class D has 228 networks.
Ques3: Range of class D?
Ans3: Range of class D (224-239).
The IP address is usually expressed as four decimal numbers, each representing eight bits, separated by periods. This is sometimes known as the dot address and, more technically, as dotted quad notation. For Class A IP addresses, the numbers would represent "network.local.local.local" for a Class C IP address, they would represent "network.network.network.local". The number version of the IP address can (and usually is) represented by a name or series of names called the domain name.
Static versus Dynamic IP Addresses-
The discussion above assumes that IP addresses are assigned on a static basis. In fact, many IP addresses are assigned dynamically from a pool. Many corporate networks and online services economize on the number of IP addresses they use by sharing a pool of IP addresses among a large number of users. If you're an America Online user, for example, your IP address will vary from one logon session to the next because AOL is assigning it to you from a pool that is much smaller than AOL's base of subscribers.