Hub-
A hub connects multiple wires in a Local Area Network (LAN) coming from different nodes. For example- the hub connects different stations in star topology. A Hub cannot filter data packets, received from different stations, so that the data packets are sent to all connected devices; which leads increasing data traffic and wastage of resources. Also, a hub cannot find best path for data packets to deliver it into destination. Hub only supports half duplex, which means at a same point of time only one way communication possible. In addition to that, a hub operates at the physical layer of the OSI/RM (Open System Interconnection / Reference Model).


Figure: Sample Hub (A Network connecting device) Figure: Sample Switch
Hubs are comes in two categories- Active Hub and Passive hub. Most hubs are active hubs, which are also called multiport repeaters. It functions in the same way as a repeater, except that it must also broadcast the regenerated signals to all connected nodes/stations rather than forwarding them to just one node/station. A passive hub provides no signal regeneration, it simply serves as a conduit for data and broadcast incoming data to every other port.
Switch-
A switch is a connecting device which is somehow works in the place of a hub. Unlike hub, switches work on the layer 2 (data link layer) of the OSI model and also follows full duplex (two-way communication at the same point of time) mode. Switches works on local area network to connect different nodes and also network types (such as Ethernet and Fast Ethernet) or networks of the same type. It filters each packet and processes it accordingly.
Repeater-
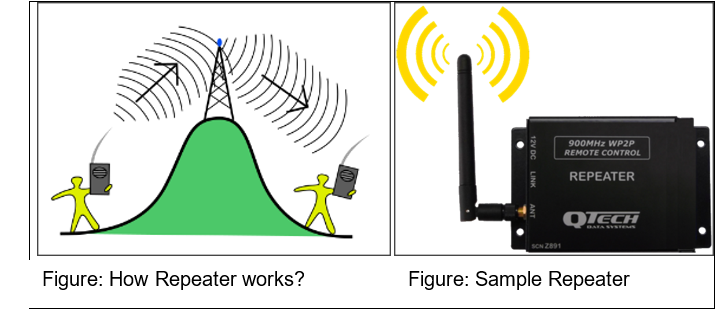
A repeater is an electronic device that receives the signal and regenerates it, so that the signal can cover longer distances. It operates at the physical layer of the OSI/RM. When the signal becomes weak, it (repeater) copies the signal bit by bit and regenerates it at the original strength.
Bridge-
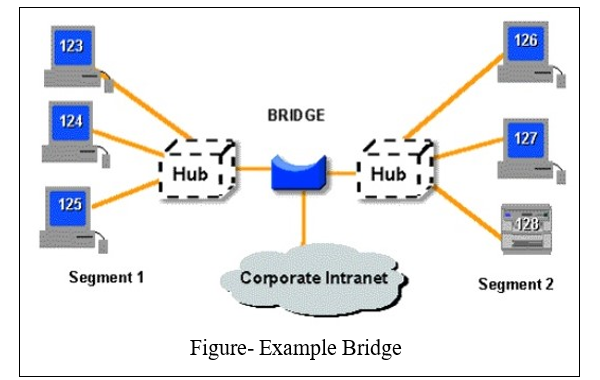
A bridge connects a local area network (LAN) to another local area network and also controls data flow between them. It works at the data-link layer of the OSI model. Bridges can operate only in half duplex mode where as a switch operates in both half or full duplex mode. Bridges are important to connect different LANs in one network, so that they can become part of the whole network. A bridge sometimes also known as ‘brouter’, it is used as a combination of router and bridge both. Brouters are the earlier implementation of the routers.
Router-
 Router is a network device (works on network layer of OSI model) that routes data packets around the network. A router has ability to connect dissimilar LANs with same protocol. It processes logical addressing information (IP address) in the Network header of a data packet. A router manages its routing table which can be built statically or dynamically. A router keeps record of the path that a data packets can use as it moves across the network, this type of records are maintained in a table known as routing table. A router can determine the destination address for the data packet and then, by using tables of defined routes (routing table), the router determines the optimal way for the data packet to forward it next or to its destination.
Router is a network device (works on network layer of OSI model) that routes data packets around the network. A router has ability to connect dissimilar LANs with same protocol. It processes logical addressing information (IP address) in the Network header of a data packet. A router manages its routing table which can be built statically or dynamically. A router keeps record of the path that a data packets can use as it moves across the network, this type of records are maintained in a table known as routing table. A router can determine the destination address for the data packet and then, by using tables of defined routes (routing table), the router determines the optimal way for the data packet to forward it next or to its destination.
Gateway-
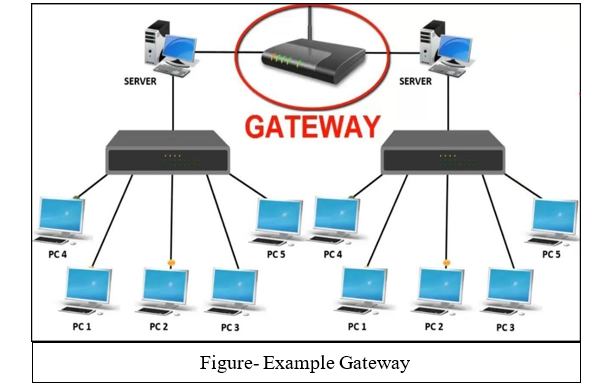 A gateway is used to connect two or more networks using different protocols together; where as a bridge is used to connect two similar types of networks. The term gateway is applied to any device or software application that can perform the function of translating data from one format to another without changing the data itself. For example- you can understand the working of a router that connects a home/local area network to WAN/Internet.
A gateway is used to connect two or more networks using different protocols together; where as a bridge is used to connect two similar types of networks. The term gateway is applied to any device or software application that can perform the function of translating data from one format to another without changing the data itself. For example- you can understand the working of a router that connects a home/local area network to WAN/Internet.