The topology of a network is the geometric representation of all the links and connected devices in a network to one another. In other words, network topology is an arrangement of network devices those are used to transmit data in a network and it also presents the structure of a network. The layout of the network connection is based on the fact that how the data is being transmitted and how are the devices linked to each other. There are the following types of network topology
Bus Topology-A bus topology is a multipoint connection, one long cable acts as a backbone to connect all the devices in a network. Nodes are connected to the bus cable by drop lines and taps. A drop line is a connection between the device and the main cable and a tap is a connector that either splices into the main cable or punctures the sheathing of a cable to create a connection with main bus. Number of taps and distance between them is limited. Basically, bus topology is popular in LAN (Local Area Network) where a greater number of nodes are connected using a single cable.
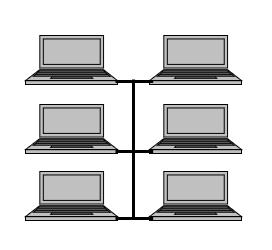 Advantages-
Advantages-
• It is easy to install/configure.
• It uses less cabling than mesh or star topology.
Disadvantages-
• Difficult to reconnection and fault isolation.
• Signal reflection at the taps can cause degradation in quality.
• Adding new devices sometimes may cause modification or replacement of the backbone.
• A fault or break in the bus/backbone cable stops all transmission in a network.
Ring Topology
In a ring topology, each device has a dedicated point-to-point connection with only the two devices on either side of it. A signal is passed along the ring in one direction, from device to device, until it reaches its destination.
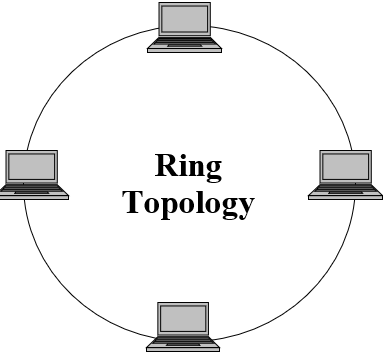 Advantages-
Advantages-
• It is easy to install and reconfigure.
• Each node has equal access to resources.
• It reduces chances of collision of data packets.
Disadvantages-
• If one node or port goes down, the entire network gets affected.
• Network is highly dependent on the wire which connects different components.
• Slower in data transmission in comparison to other networks.
Mesh Topology-
In a mesh topology, every device (Computer or node) has a dedicated point-to-point link to every other device. The term dedicated means that the link carries data traffic only between the two devices it connects.
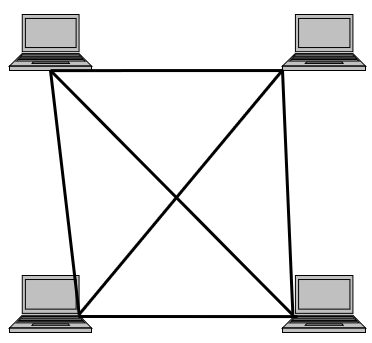
Advantages-
• A mesh topology uses dedicated links which guarantees each connection can carry its own data load.
• It eliminates the data traffic problems because of dedicated links.
• A mesh topology is robust because if one link becomes unusable, it does not incapacitate the entire system.
• It provides secure communication among stations, when each message travels along a dedicated line, only the intended recipient sees it.
• A point-to-point links make fault identification and fault isolation easy.
Disadvantages-
• Amount of cabling and input/output ports used is too much.
• Installation and reconnection is difficult.
• It is too expensive; because hardware (cable and I/O ports) required connecting each link is much larger.
• It is usually implemented in a limited fashion.
Star Topology-
In a star topology, each device has a dedicated point-to-point link only to a central controller, usually called a hub or switch. The devices are not directly linked to one another. It does not allow direct data traffic/transmission between devices. The central controller acts as an exchange: If one device wants to send data to another, it sends the data to the controller, which then relays the data to the other connected device.
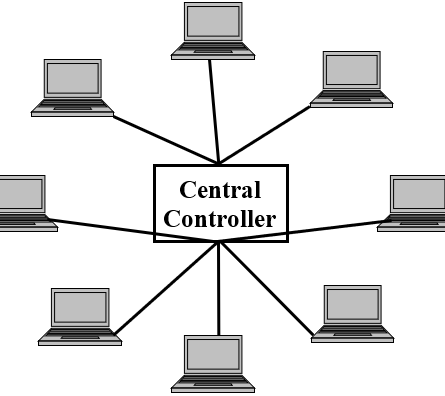
Advantages-
• A star topology is less expensive than a mesh topology.
• In a star topology, each device needs only one link and one I/O port to connect it to any number of other devices.
• Easy to install and reconfigure, if one link fails, only that link is affected.
• It needs less cabling and easy to fault identification & isolation.
Disadvantages-
• Fully dependent on one single point, called the central hub/switch.
• If the central hub goes down, the whole system is unable to work.