Indian banking system has divided in two major schedules: (i) Scheduled Banks (ii) Non-Scheduled Banks.
Scheduled Banks-
The banks which have been scheduled in second scheduled of Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Act, 1934 are known as scheduled banks. As per the schedule, these banks must comply of the following:
• Paid-Up capital and collected funds should not be less than Rs Five Lakhs.
• Any activity of the bank should not affect the interest of the customers.
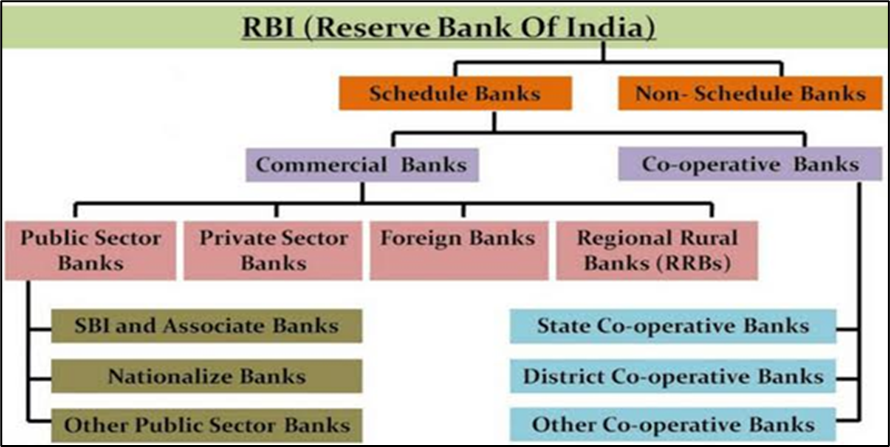
Figure 7.1 Bank Classification
The banks belong to this category are comprised: (i) Commercial Banks (ii) Cooperative Banks.
Further the commercial banks can be divided under the following:
a) Public Sector Banks- Banks which are owned by government (i.e. more than 51% of stake) are known as public sector bank. Currently, there are 21 public sector banks in India from which 19 are nationalized. For e.g. SBI, PNB and BOB are top most leading public sector banks in India.
b) Private Sector Banks- Are those banks owned by private individuals or institutions. These types of banks are also listed under Indian companies Act 1956 as a limited company. For e.g. ICICI and HDFC are the top leading private sector banks of our country.
c) Foreign Banks- Are those banks which are not listed as an Indian company or organization. These banks are incorporated outside the country and they just have some branches in our country. Finally, we can say they are not operated from our country. Some examples of foreign banks are HSBC, etc.
d) Regional Rural Banks- Since the middle of 1970’s, Regional Rural Banks came into existence in India. These banks were set up with the specific objective of providing credit and facilities of deposits especially to small and marginal farmers, agricultural labor and artisans and small enterprises. Rural development in respect of agriculture, trade, commerce and industry is the prime responsibility of Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) of India. Banks which are operated at state level but they are governed under the regulations of Reserve Bank of India. Some examples of RRB are Uttarakhand Gramin Bank etc.
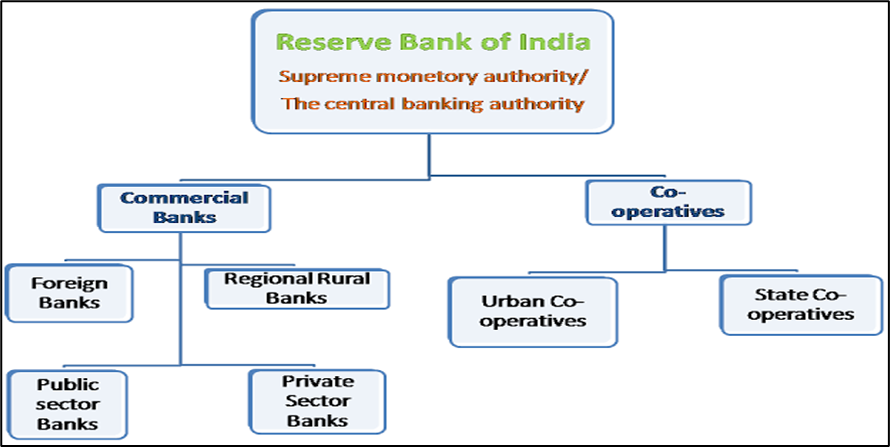
Figure 7.2 Indian Banking System
Non-Scheduled Banks
The banks which are listed under clause (c) of section 5 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 (10 of 1949) are known as Non-Scheduled Banks.